Щелковая и Конусная дробилки — распространённое дробильное оборудование, но чем они отличаются? Какую из них выбрать? Давайте рассмотрим их различия и преимущества.
Сравнение щелковой дробилки с конусной дробилкой
Щелковая дробилка в первую очередь осуществляет первичное дробление, разбивая крупные камни (до 1500 мм) на более мелкие куски (менее 100 мм) для дальнейшей обработки.
Конусная дробилка, в свою очередь, дробит камни среднего размера и в основном выполняет функцию вторичного дробления. Она специализируется на дроблении твёрдых камней и оснащена предохранительным механизмом, который срабатывает для защиты оборудования от повреждений.
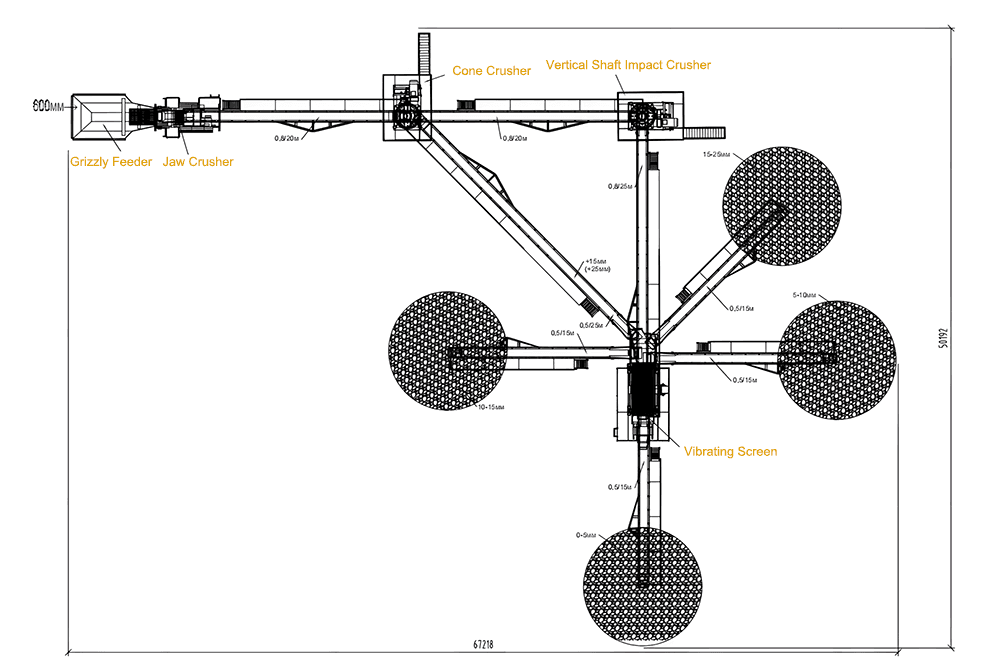
Основные различия между щелковой и конусной дробилкой
Знание этих различий поможет вам выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант.
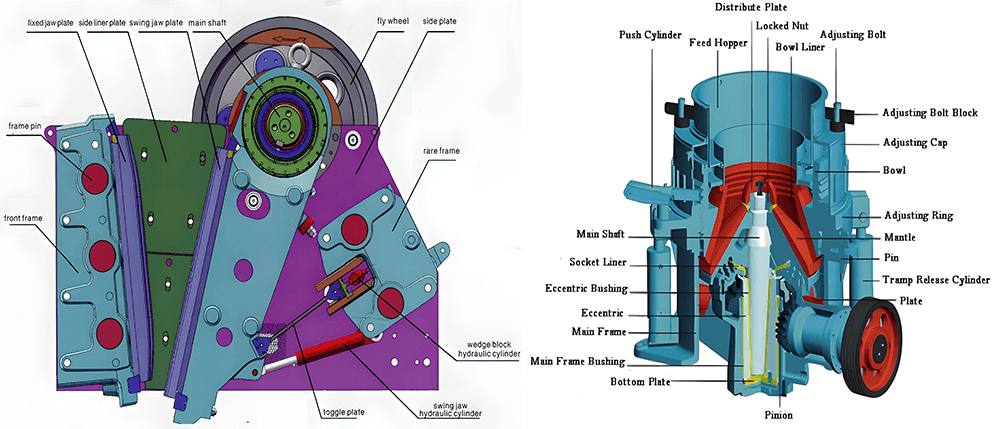
1. Общая структура: щелковая дробилка VS конусная дробилка
Щелковая дробилка:
- Она состоит из рамы, передаточного механизма, регулировочного устройства, натяжного устройства, предохранительного устройства и системы смазки.
- Передаточный механизм соединяет всю конструкцию и играет ключевую роль.
- Он использует сжимающее усилие для эффективного дробления твёрдых камней с высокой степенью дробления.
Конусная дробилка:
- Состоит из рамы, гидравлических компонентов, головки, кожуха, главного вала, промежуточного вала, подающей плиты, опорного кольца, гнезда, эксцентрика, шестерни и т.д.
- Основными износостойкими деталями являются дробящие стенки.
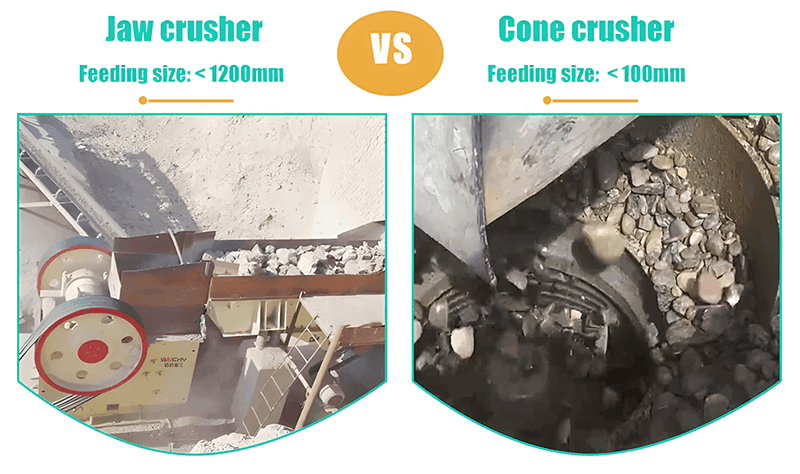
2. Требования к подаче: щелковая дробилка VS конусная дробилка
Щелковая дробилка:
- Обрабатывает широкий диапазон размеров исходного материала.
- Большие щековые дробилки работают с материалом крупностью более 600 мм (до 1200 мм), средние — с материалом 300–600 мм, а малые — с материалом менее 300 мм.
Конусная дробилка:
- Требует меньшего размера исходного материала, обычно менее 450 мм (зависит от модели).
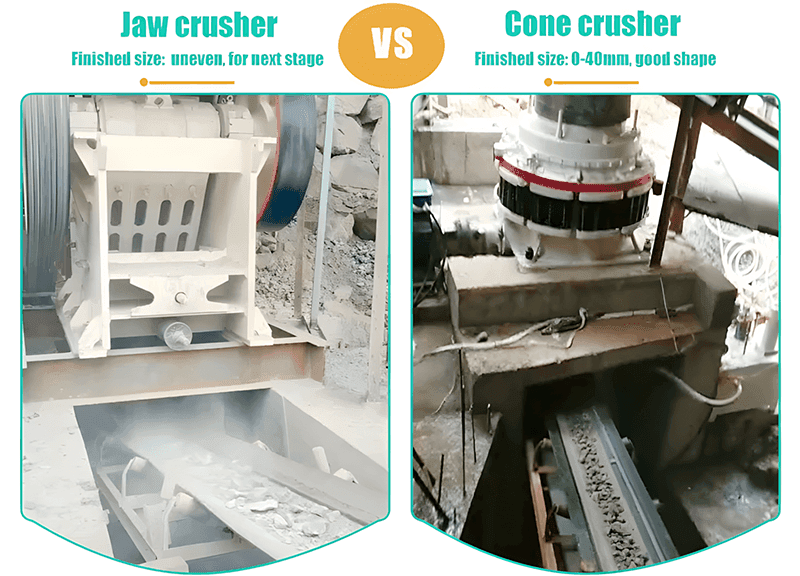
3. Форма готового продукта
Щелковая дробилка:
- Идеально подходит для первичного дробления, обеспечивая высокую производительность и более крупные размеры выходного материала.
- При необходимости также подходит для вторичного дробления.
Конусная дробилка:
- Она обеспечивает вторичное и третичное дробление, образуя более мелкие частицы однородной формы.
- Непрерывно измельчает материал до тех пор, пока он не пройдет через узкое разгрузочное отверстие.
4. Сравнение цен
Из-за сложной конструкции и износостойких деталей конусная дробилка стоит значительно дороже щековой.
- Объем конусной дробилки в 2-3 раза выше щековой.
- При равной производительности конусная дробилка весит в 1-2 раза тяжелее.
- Ее монтаж и обслуживание также сложнее.
5. Пример: сравнение дробилок производительностью 300 тонн в час
При сравнении установок производительностью 300 тонн в час:
- Конусная дробилка весит примерно вдвое больше щековой, что увеличивает затраты на строительство и обслуживание.
- Щелковые дробилки обеспечивают более высокую степень дробления, тогда как конусные дробилки более эффективно обрабатывают твердые материалы.
| Model | Jaw Crusher | Cone Crusher |
|---|---|---|
| Max feed size | 630 mm | 215 mm |
| Output size | 60-150 mm | 25-60 mm |
| Capacity | 110-380 TPH | 180-360 TPH |
| Motor power | 110 kW | 160 kW |
| Weight | 29 tons | 60 tons |
Заключение
Как щелковые, так и конусные дробилки обладают уникальными преимуществами. Щелковые дробилки превосходны на первичном дроблении благодаря высокой производительности, в то время как конусные дробилки обеспечивают более мелкий выход на вторичной и третичной стадиях дробления. Выбор зависит от твёрдости материала, желаемого размера выходного материала, производственных потребностей и бюджета. Перед покупкой проконсультируйтесь со специалистом для получения профессиональной консультации.
Часто задаваемые вопросы (FAQ)
В: Какой тип дробилки лучше — конусная или щелковая?
О: Щелковые дробилки обрабатывают камни от мягкого известняка до твёрдого гранита, а конусные дробилки используют вращающийся конус для более тонкого дробления.
В: Зачем использовать конусную дробилку?
О: Они эффективно перерабатывают породы средней и высокой твёрдости, потребляя меньше энергии, сохраняя высокую надёжность и обеспечивая значительное измельчение.
В: Насколько тонко дробит конусная дробилка?
О: Конусные дробилки обычно перерабатывают материалы предварительно заданного размера (100–200 мм) в более мелкие, хорошо рассортированные материалы.
В: Какая дробилка лучше всего подходит для камня?
О: Выбор оптимальной дробилки зависит от твёрдости материала, требуемого размера выходного материала и производственных потребностей. Доступны щелковые, конусные, ударные, валковые, молотковые, дробилки с вертикальным валом (VSI) и мобильные дробильные установки.
В: Каковы преимущества конусных дробилок?
О: Конусные дробилки обеспечивают высокую эффективность, равномерный размер частиц, низкое энергопотребление и надёжную работу. Они отлично справляются со вторичным и третичным дроблением, хорошо справляются с твердыми материалами и оснащены встроенной защитой от перегрузки.
В: Каков принцип работы конусной дробилки?
О: Конусная дробилка работает, сжимая материал между вращающейся конусной плитой и неподвижной вогнутой подушкой. Эксцентриковое движение создаёт сжатие, дробя горную породу на более мелкие, равномерно распределенные частицы.
В: Используются ли конусные дробилки для первичного дробления?
О: Обычно нет — конусные дробилки в основном предназначены для вторичного/третичного дробления. Однако некоторые модели (например, дробилка CC400S) могут использоваться для первичного дробления в особых случаях.
В: Какая дробилка лучше всего подходит для твёрдых пород?
О: Для твёрдых пород (например, гранита, базальта) идеально подходят щековые дробилки (первичное дробление) и конусные дробилки (вторичное дробление). Высокая степень измельчения и высокая сила сжатия конусных дробилок делают их особенно эффективными.
В: Почему именно щелковые дробилки?
О: Щелковые дробилки экономичны, просты в обслуживании и универсальны для первичного дробления. Они способны обрабатывать крупные куски исходного материала (до 1500 мм) и прочные материалы, что делает их идеальным решением для первичного дробления горных пород.
В: Как обслуживать конусную дробилку?
О: Регулярно проверяйте смазку (уровень масла/фильтры), осматривайте изнашиваемые детали (подвижный / неподвижный конуса), следите за натяжением ремня и очищайте от пыли/мусора. Планируйте время простоя для замены футеровки и проверки центровки, чтобы предотвратить поломки.
